Marketing is all about showing up where your audience is. But what happens when your audience isn’t quite ready to commit? That’s where remarketing and retargeting come into play. These two strategies may sound similar, but their unique approaches can make or break your campaign’s effectiveness. Let’s dive into what sets them apart and how you can use them to drive results.
1. Introduction to Remarketing and Retargeting
Digital marketing is all about connections. Whether you’re selling shoes or software, staying in your audience’s mind is essential. Remarketing and retargeting offer ways to do just that, albeit through slightly different tactics.
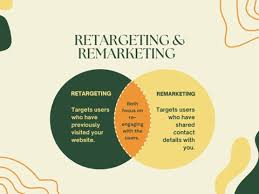
- Remarketing: This typically involves re-engaging users via email. Think of it as a gentle nudge, reminding someone about your product after they’ve visited your site.
- Retargeting: This leans on display ads to recapture attention. It uses cookies to show tailored ads on websites or social media.
Why are these methods so important? Research shows that 97% of people who visit a website leave without converting. Remarketing and retargeting help bridge that gap, guiding potential customers back to you.
2. The Core Differences Between Remarketing and Retargeting
Key Features of Remarketing
- Focuses on email campaigns
- Works best for reconnecting with existing customers
- Personalized messages are a key strength
Key Features of Retargeting
- Relies on cookies or tracking pixels
- Displays ads across various platforms
- Targets a broader audience segment
Channels Used: Email vs. Display Ads
- Remarketing campaigns are heavy on email.
- Retargeting shines on platforms like Google Display Network and Facebook.
Behavioral vs. Contextual Targeting
- Retargeting targets behaviors, like visiting a specific product page.
- Remarketing uses data like purchase history to deliver more relevant messages.
3. How Remarketing Works
Collecting User Data
Marketers often rely on customer databases to craft targeted campaigns. These can include past purchases, browsing behaviors, or abandoned carts.
Building Email Campaigns
Email remarketing campaigns often focus on:
- Cart Abandonment: Reminding users of items left behind
- Upselling: Suggesting upgrades or complementary products
- Seasonal Promotions: Re-engaging during peak shopping times
Examples of Effective Remarketing Campaigns
- E-commerce: Sending discounts to users who abandoned their carts
- SaaS: Offering free trials to users who didn’t convert during a demo
- Travel: Reminding users about flights they searched for
htmlCopy code<ul>
<li>“Still thinking about this? Here’s 10% off!”</li>
<li>“Your dream vacation is just a click away.”</li>
<li>“We noticed you liked [Product]. Here’s a deal!”</li>
</ul>
Benefits of Remarketing
- Higher conversion rates
- Personalized customer engagement
- Cost-effective for nurturing existing leads
4. How Retargeting Works
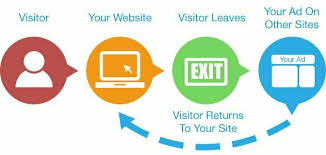
Using Cookies and Tracking Pixels
These tools allow marketers to “follow” users online, serving ads based on their browsing history.
Display Ad Creation Strategies
Successful retargeting campaigns use:
- Eye-catching visuals
- Clear calls to action (CTAs)
- Dynamic content that adapts to user behavior
Examples of Successful Retargeting Campaigns
- Amazon: “You left this in your cart!” ads
- Booking.com: Reminding users about hotels they viewed
- Retail brands: Flash sale ads to create urgency
Benefits of Retargeting
- Recaptures lost traffic
- Increases brand recall
- Works across multiple platforms
5. When to Use Remarketing
Best Scenarios for Remarketing Campaigns
Remarketing shines when you need to re-engage with people who are already familiar with your brand but haven’t taken the next step. For example:
- Abandoned Carts: A staggering 69% of shopping carts are abandoned. Sending a follow-up email with a discount or a gentle reminder often works wonders.
- Loyalty Programs: Encourage repeat customers by offering exclusive deals or early access to new products.
- Upselling Opportunities: If someone recently purchased a phone, send an email promoting accessories like cases or chargers.
Targeting Existing Customers vs. Potential Leads
- Existing Customers: Remarketing campaigns can introduce new products, encourage reviews, or provide loyalty rewards.
- Potential Leads: These campaigns can bring back users who showed interest but didn’t convert.
Budget Considerations
Remarketing often requires less budget than retargeting. Email campaigns cost less than display ads, especially when targeting an existing database.
Industries That Benefit Most
Remarketing is particularly effective for industries with high customer lifetimes, such as:
- E-commerce
- Travel and Hospitality
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
6. When to Use Retargeting
Ideal Situations for Retargeting Ads
Retargeting is your go-to strategy for bringing back traffic that hasn’t engaged deeply yet. Scenarios include:
- Browsing Without Converting: Users who looked at products or services but didn’t act.
- Event Promotions: Retarget users who visited an event page but didn’t register.
- Competitor Visitors: Using platforms like Google Ads, you can target users who visited competitor sites.
Re-engaging Abandoned Cart Users
Sometimes a display ad, rather than an email, works better for re-engagement. Retargeting ads can use visuals to remind users what they left behind.
Ad Placement Strategies
- Use high-traffic platforms like Google Display Network or social media channels like Facebook and Instagram.
- Focus on mobile-optimized ads since a significant portion of traffic is mobile-based.
Measuring Success Metrics
Track the performance of retargeting campaigns using these metrics:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Conversion Rate
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA)
7. Combining Remarketing and Retargeting for Maximum Impact
Creating an Integrated Strategy
To get the best of both worlds, combine email campaigns with targeted display ads. For example:
- Send a personalized email after a cart is abandoned.
- Follow up with retargeting ads showing the same products.
Tools and Platforms for Execution
- Remarketing Tools: Mailchimp, HubSpot, or Klaviyo.
- Retargeting Tools: Google Ads, Facebook Ads Manager, or AdRoll.
Avoiding Overexposure: Frequency Capping
While persistence pays off, overloading users with ads can be counterproductive. Use frequency caps to limit the number of times users see your ads.
Case Studies of Brands Combining Both Strategies
- Amazon: Uses emails for recommendations and display ads for retargeting.
- Airbnb: Sends personalized emails after a search and backs it up with retargeting ads featuring alternative listings.
8. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Privacy Concerns and Regulations
- GDPR and CCPA regulations restrict how user data can be used.
- To stay compliant:
- Obtain explicit consent for cookies.
- Provide clear opt-out options in email campaigns.
Campaign Fatigue: How to Keep Audiences Engaged
- Rotate creatives frequently to keep ads fresh.
- Test different email copy and subject lines.
Measuring ROI for Both Strategies
- Use Google Analytics to track conversions from retargeting ads.
- For remarketing, measure email open rates, click-throughs, and conversions.
Tips for Improving Campaign Performance
- Segment your audience for more personalized outreach.
- Use A/B testing to optimize ads and email campaigns.
- Regularly review and refine your targeting criteria.
9. Conclusion
Remarketing and retargeting are two sides of the same coin. Both aim to bring users back into your sales funnel, but they approach it differently. Remarketing excels at nurturing existing relationships, while retargeting is perfect for rekindling interest in new leads.
The best results often come from combining these strategies thoughtfully. By understanding their differences, leveraging the right tools, and optimizing campaigns for your target audience, you can maximize your ROI and create meaningful customer connections.
10. FAQs
What is the main difference between remarketing and retargeting?
Remarketing focuses on email campaigns to re-engage existing customers, while retargeting uses display ads to reach people who visited your site but didn’t convert.
Are remarketing and retargeting suitable for small businesses?
Yes! Both strategies are highly scalable. Small businesses can start with affordable email campaigns for remarketing and expand to retargeting ads as their audience grows.
What tools can I use for remarketing and retargeting?
- Remarketing: Tools like Mailchimp, ActiveCampaign, or HubSpot.
- Retargeting: Platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, or AdRoll.
How do privacy laws affect these strategies?
Laws like GDPR require you to obtain user consent for tracking cookies and provide opt-out options for email campaigns. Transparency is key to staying compliant.
Can I use both strategies simultaneously?
Absolutely! Combining remarketing and retargeting ensures you reach customers at different stages of their journey, increasing your chances of conversion.
